The Weathering Deposition and Erosion Worksheet invites you on an enlightening journey into the captivating world of Earth’s surface processes. From the subtle artistry of weathering to the powerful forces of deposition and erosion, this worksheet will guide you through the dynamic interplay that shapes our planet’s landscapes.
As you delve into this exploration, you will uncover the intricate mechanisms of rock breakdown, the transport and accumulation of sediments, and the erosive forces that sculpt our planet’s surface. Prepare to be captivated by the interplay of natural forces that have molded Earth’s visage over eons.
Weathering
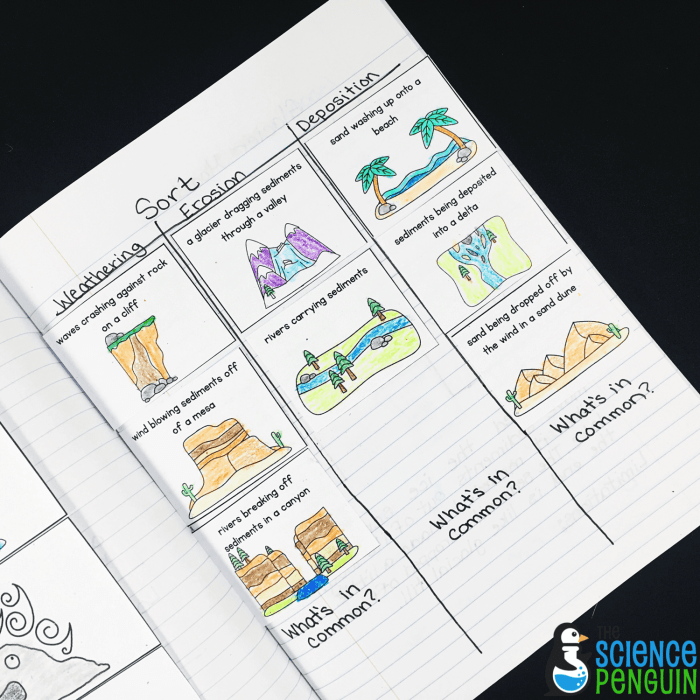
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks and minerals on the Earth’s surface into smaller pieces. It is a key part of the rock cycle, which is the process by which rocks are formed, broken down, and reformed over time.
There are two main types of weathering: mechanical weathering and chemical weathering. Mechanical weathering is the physical breakdown of rocks and minerals into smaller pieces. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including temperature changes, freezing and thawing, and abrasion.
Mechanical Weathering
- Temperature changes: When rocks are heated, they expand. When they cool, they contract. This can cause the rocks to crack and break apart.
- Freezing and thawing: When water gets into cracks in rocks and freezes, it expands. This can cause the cracks to widen and the rocks to break apart.
- Abrasion: Abrasion is the process of wearing away rocks and minerals by friction. This can be caused by wind, water, or ice.
Chemical weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals by chemical reactions. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including water, oxygen, and acids.
Chemical Weathering
- Water: Water can dissolve minerals in rocks and minerals. This can cause the rocks to become weaker and more susceptible to mechanical weathering.
- Oxygen: Oxygen can react with minerals in rocks and minerals to form new minerals. This can cause the rocks to change color and become more brittle.
- Acids: Acids can dissolve minerals in rocks and minerals. This can cause the rocks to become weaker and more susceptible to mechanical weathering.
Weathering is a complex process that can have a significant impact on the Earth’s surface. It can create new landforms, such as mountains and valleys, and it can also expose valuable minerals and ores.
Deposition
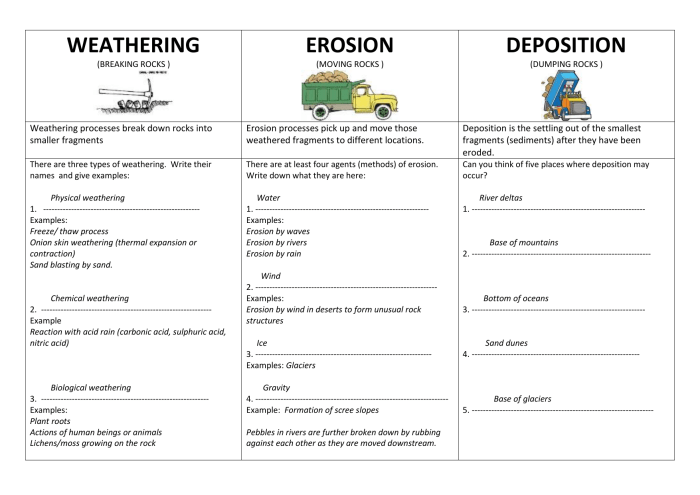
Deposition is the process of laying down sediments. Sediments are bits of rock, mineral, or organic matter that have been transported by wind, water, or ice.
Deposition occurs when the energy of the wind, water, or ice that is transporting the sediments decreases. This can happen when the wind or water slows down, or when the ice melts. When the energy decreases, the sediments settle out of the wind, water, or ice and are deposited on the ground.
Deposition is an important part of the rock cycle. It is the process by which new rocks are formed. When sediments are deposited, they are often compacted and cemented together by minerals. Over time, these sediments can turn into rock.
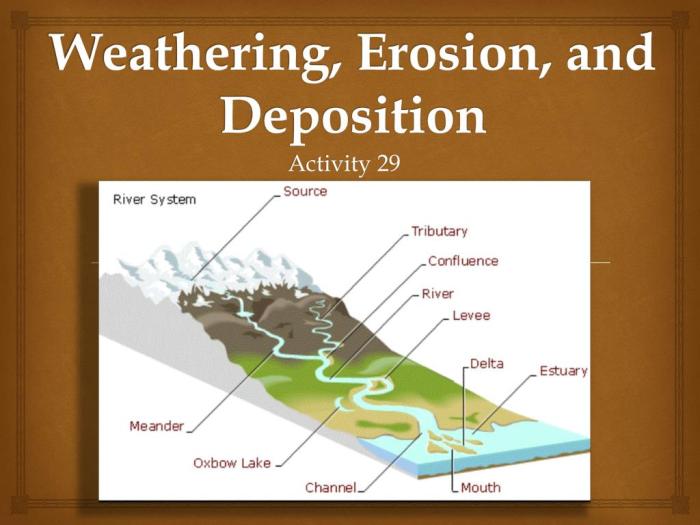
How Sediments are Transported and Deposited
Sediments can be transported by wind, water, or ice. Wind can transport small particles of sediment, such as sand and dust. Water can transport larger particles of sediment, such as gravel and boulders. Ice can transport very large particles of sediment, such as boulders and even entire mountains.
When sediments are deposited, they are often sorted by size. The largest particles are deposited first, followed by the smaller particles. This is because the larger particles are more difficult to transport than the smaller particles.
Depositional Environments
Deposition can occur in a variety of environments, including deserts, beaches, rivers, and glaciers. In deserts, wind can transport sand and dust and deposit it in dunes. On beaches, waves can transport sand and deposit it on the beach. In rivers, water can transport sediment and deposit it on the riverbanks or in the riverbed.
In glaciers, ice can transport sediment and deposit it in moraines.
Erosion: Weathering Deposition And Erosion Worksheet
Erosion is the process of wearing away the Earth’s surface. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including wind, water, and ice.
Types of Erosion
There are three main types of erosion: water erosion, wind erosion, and glacial erosion.
- Water erosion: Water erosion is the most common type of erosion. It is caused by the flow of water over the Earth’s surface. Water erosion can be caused by rainfall, runoff, and flooding.
- Wind erosion: Wind erosion is caused by the movement of wind over the Earth’s surface. Wind erosion can be caused by strong winds, such as hurricanes and tornadoes, or by gentle breezes.
- Glacial erosion: Glacial erosion is caused by the movement of glaciers over the Earth’s surface. Glacial erosion can be caused by the weight of the glacier, or by the movement of ice over the ground.
Impact of Erosion
Erosion can have a significant impact on the environment. It can cause soil loss, which can lead to decreased agricultural productivity. Erosion can also cause sedimentation, which can clog rivers and streams and damage aquatic ecosystems.
Controlling Erosion, Weathering deposition and erosion worksheet
There are a number of ways to control erosion. These methods include:
- Planting trees and other vegetation: Trees and other vegetation can help to hold soil in place and reduce erosion.
- Building terraces and contour plowing: Terraces and contour plowing can help to slow down the flow of water and reduce erosion.
- Using erosion control blankets: Erosion control blankets can be used to cover bare soil and help to prevent erosion.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary goal of the Weathering Deposition and Erosion Worksheet?
To provide a comprehensive understanding of the processes involved in weathering, deposition, and erosion, and their impact on Earth’s surface.
How does the worksheet facilitate learning?
Through a combination of informative text, engaging questions, and hands-on activities, the worksheet encourages active learning and promotes a deeper comprehension of the subject matter.
What is the significance of studying weathering, deposition, and erosion?
These processes play a crucial role in shaping Earth’s landscapes, influencing ecosystems, and providing insights into the planet’s geological history.