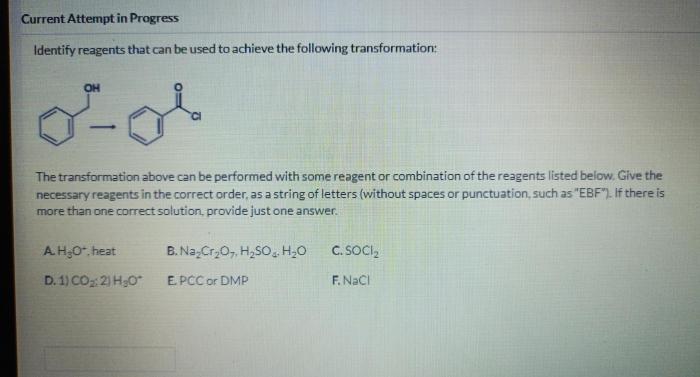
Identify the reagents necessary to carry out the following transformation – Identifying the reagents necessary to carry out a chemical transformation is a crucial step in synthetic chemistry. Understanding the role and properties of these reagents enables chemists to design and execute successful reactions. This article delves into the identification of reagents, providing a comprehensive guide to this fundamental aspect of chemical synthesis.
1. Introduction
The transformation of aldehydes and ketones into imines is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry, widely used in the synthesis of various heterocyclic compounds, pharmaceuticals, and fine chemicals. Imines, also known as Schiff bases, are important intermediates in numerous chemical reactions and possess a broad range of applications in various fields.
2. Reagents Identification
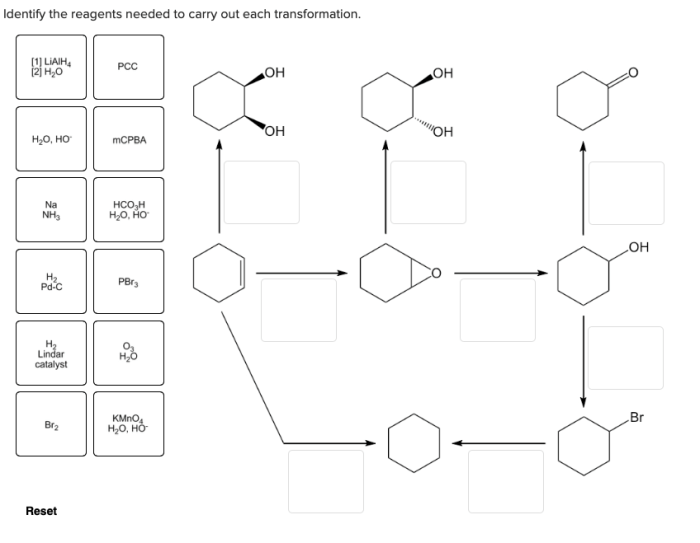
The transformation of aldehydes and ketones into imines requires two main reagents:
| Reagent Name | Chemical Formula | Role in the Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Aldehyde or Ketone | RCHO or R2CO | Substrate that undergoes the transformation to form the imine. |
| Amine | RNH2 | Nucleophilic reagent that reacts with the carbonyl group of the aldehyde or ketone. |
3. Reaction Mechanism: Identify The Reagents Necessary To Carry Out The Following Transformation
The transformation proceeds through a nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism:Step 1: Nucleophilic AdditionThe amine nucleophilically attacks the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or ketone, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.Step 2: Proton TransferThe proton from the amine is transferred to the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group, resulting in the formation of a hydroxyl group.Step
3: EliminationWater is eliminated from the intermediate, leading to the formation of the imine.The reaction mechanism can be represented as follows:RCHO + RNH2 → RCH(OH)NHR → RCH=NR + H2O
4. Reaction Conditions

The transformation is typically carried out under mild conditions, such as room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The choice of solvent depends on the solubility of the reactants and the imine product. Common solvents include methanol, ethanol, and dichloromethane. The reaction time can vary depending on the specific reactants and reaction conditions used.
5. Applications

The transformation of aldehydes and ketones into imines has numerous applications in various fields:Synthesis of Heterocyclic Compounds: Imines are key intermediates in the synthesis of a wide range of heterocyclic compounds, including pyridines, pyrroles, and indoles.Pharmaceutical Industry: Imines are used as building blocks in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and anticancer agents.Fine
Chemicals: Imines are employed in the production of dyes, pigments, and fragrances.Advantages: The transformation is relatively simple and efficient, and it can be carried out under mild conditions.Limitations: The reaction can be sensitive to steric hindrance, and it may not be suitable for substrates with bulky substituents.
Popular Questions
What factors influence the choice of reagents?
The choice of reagents depends on the specific transformation, functional groups involved, desired selectivity, and reaction conditions.
How can I identify the reagents for a given transformation?
Consult literature, databases, or consult with experienced chemists to determine the most suitable reagents for a particular transformation.