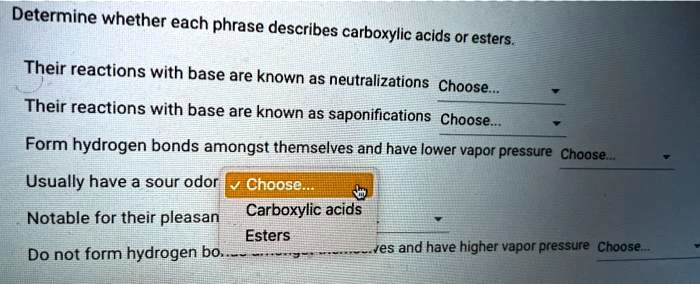
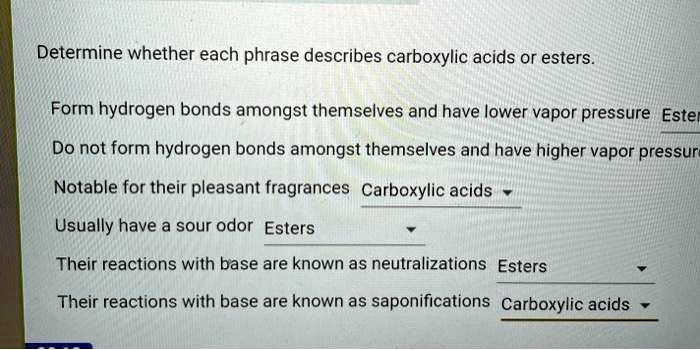
Determine whether each phrase describes carboxylic acids or esters. – Embarking on an exploration of the defining characteristics of carboxylic acids and esters, this discourse delves into a comparative analysis of their chemical structures, physical properties, and chemical reactivity. By examining a series of phrases, we aim to establish a clear understanding of the distinctions between these two classes of organic compounds.
Carboxylic acids, characterized by their carboxyl group (-COOH), exhibit a unique set of properties that differentiate them from esters. Esters, on the other hand, formed by the reaction of carboxylic acids with alcohols, possess their own distinct chemical and physical attributes.
Through a comprehensive comparison, we will uncover the fundamental differences that distinguish these two important functional groups.
Carboxylic Acid Identification
Carboxylic acids are a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are named according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature, which assigns a name based on the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain and the presence of any functional groups.
Chemical Structure
The carboxyl group consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the same carbon atom. The carbon atom in the carboxyl group is sp 2hybridized and forms three sigma bonds: one with each of the oxygen atoms and one with the alkyl or aryl group.
Examples and IUPAC Nomenclature
- Methanoic acid(formic acid): HCOOH
- Ethanoic acid(acetic acid): CH 3COOH
- Propanoic acid: CH 3CH 2COOH
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Carboxylic acids are typically colorless liquids or solids with a pungent odor.
- They have relatively high boiling points due to strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Carboxylic acids are weak acids and can undergo dissociation in water to form carboxylate anions and hydrogen ions.
- They undergo a variety of reactions, including esterification, amidation, and halogenation.
- Methyl acetate: CH 3COOCH 3
- Ethyl propanoate: CH 3CH 2COOCH 2CH 3
- Phenyl benzoate: C 6H 5COOC 6H 5
- Esters are typically colorless liquids or solids with pleasant odors.
- They have lower boiling points than carboxylic acids due to weaker intermolecular forces.
- Esters are generally unreactive compared to carboxylic acids.
- They can undergo hydrolysis, saponification, and transesterification reactions.
- Boiling points: Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than esters due to stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Odor: Carboxylic acids have pungent odors, while esters typically have pleasant odors.
- Acidity: Carboxylic acids are weak acids, while esters are generally unreactive.
- Hydrolysis: Carboxylic acids undergo hydrolysis slowly, while esters undergo hydrolysis more readily.
- Saponification: Carboxylic acids do not undergo saponification, while esters undergo saponification to form salts and alcohols.
Ester Identification
Esters are organic compounds formed by the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol. They are named according to the IUPAC nomenclature, which assigns a name based on the alcohol and carboxylic acid used in their synthesis.
Chemical Structure
Esters have the general formula RCOOR’, where R is the alkyl or aryl group derived from the carboxylic acid and R’ is the alkyl or aryl group derived from the alcohol.
Examples and IUPAC Nomenclature
Physical and Chemical Properties
Comparative Analysis of Carboxylic Acids and Esters: Determine Whether Each Phrase Describes Carboxylic Acids Or Esters.
Chemical Structures
Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), while esters contain an ester group (-COOR’). The ester group is formed by the reaction of the hydroxyl group of an alcohol with the carboxyl group of a carboxylic acid.
Physical Properties
Chemical Reactivity, Determine whether each phrase describes carboxylic acids or esters.
Determining Phrase Descriptions
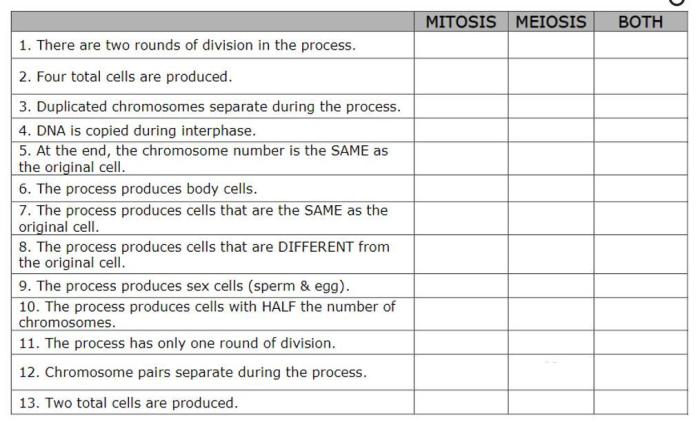
| Phrase | Description | Carboxylic Acid | Ester |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic | Describes a compound that can donate a hydrogen ion | True | False |
| Contains a carboxyl group | Describes a compound that has a
|
True | False |
| Reacts with bases to form salts | Describes a compound that can undergo a neutralization reaction | True | False |
| Has a fruity odor | Describes a compound that typically has a pleasant odor | False | True |
| Undergoes hydrolysis to form an alcohol and a carboxylic acid | Describes a compound that can be broken down into its constituent parts | True | True |
User Queries
What is the key structural difference between carboxylic acids and esters?
Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (-COOH), while esters have an ester group (-COOR), where R represents an alkyl or aryl group.
How can you distinguish between carboxylic acids and esters based on their physical properties?
Carboxylic acids typically have higher boiling points and lower solubility in water than esters due to the presence of hydrogen bonding in carboxylic acids.
What is the characteristic chemical reaction of carboxylic acids?
Carboxylic acids undergo esterification reactions with alcohols to form esters.