Embark on an educational journey with Eureka Math Geometry Module 1, where foundational concepts and essential skills intertwine to empower students. Aligned with Common Core State Standards, this module sets the stage for a deeper understanding of geometry.
Delve into effective teaching strategies, explore the power of manipulatives and visual aids, and discover how technology enhances engagement and learning. Together, we’ll navigate the challenges, connect concepts to real-world applications, and design engaging lesson plans that ignite students’ curiosity.
Key Concepts and Skills in Eureka Math Geometry Module 1
Eureka Math Geometry Module 1 lays the foundation for understanding geometric concepts and shapes. It introduces fundamental ideas that will serve as building blocks for more complex geometry in later grades.
Key concepts covered in Module 1 include:
- Basic geometric shapes (circles, squares, triangles, rectangles, and trapezoids)
- Properties of these shapes (e.g., number of sides, angles, vertices)
- Classifying shapes based on their properties
- Composing and decomposing shapes
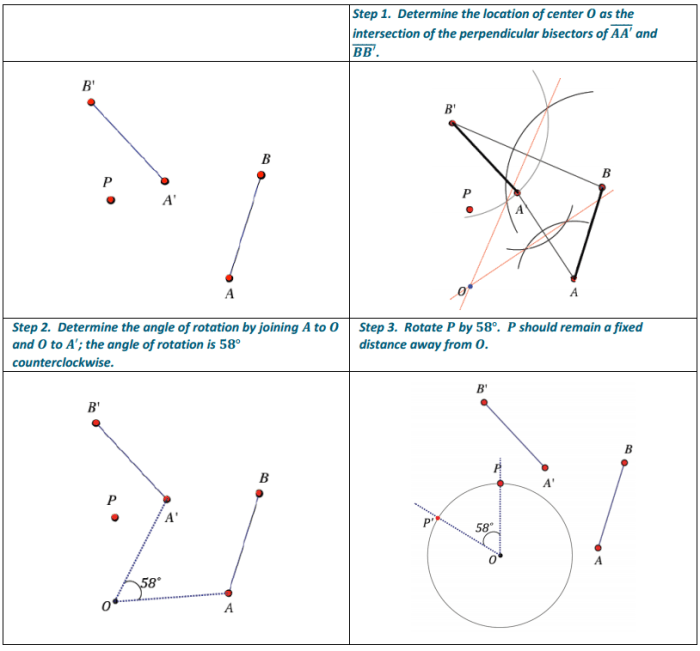
- Transformations (translations, rotations, and reflections)
Students will develop key skills such as:
- Identifying and describing geometric shapes
- Using geometric vocabulary accurately
- Applying geometric properties to solve problems
- Visualizing and manipulating shapes mentally
- Reasoning about geometric relationships
Eureka Math Geometry Module 1 is aligned with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics (CCSS-M), specifically the following domains:
- Geometry (G)
- Measurement and Data (MD)
Strategies for Eureka Math Geometry Module 1
Eureka Math Geometry Module 1 introduces students to the basics of geometry. To make this learning journey effective, it’s crucial to employ a range of teaching strategies that cater to diverse learning styles and engage students in meaningful ways.
In this module, manipulatives and visual aids play a pivotal role in helping students visualize and understand geometric concepts. Tangible materials, such as blocks, tiles, and protractors, provide hands-on experiences that solidify abstract ideas.
Effective Teaching Strategies
- Incorporate Hands-on Activities:Engage students with hands-on activities that allow them to explore geometric shapes and relationships physically.
- Use Visual Aids:Utilize diagrams, charts, and models to illustrate geometric concepts visually, making them more accessible and relatable.
- Encourage Collaborative Learning:Facilitate group discussions and peer interactions to promote knowledge sharing and deeper understanding.
- Provide Clear and Concise Instructions:Ensure that students have a clear understanding of the concepts and procedures before engaging in activities.
- Offer Varied Practice Opportunities:Provide ample practice opportunities through problem-solving, games, and worksheets to reinforce learning.
Differentiation
Differentiation is key to ensuring that all students have access to meaningful learning experiences. Here are some strategies to cater to diverse learner needs:
- Adjust Pacing:Adapt the pace of instruction to accommodate different learning styles and levels of understanding.
- Provide Tiered Activities:Offer activities with varying levels of complexity to challenge all students.
- Use Flexible Grouping:Group students strategically to promote peer support and targeted instruction.
- Offer Multiple Representations:Present concepts in various formats (e.g., visual, auditory, kinesthetic) to cater to different learning preferences.
Assessment and Evaluation in Eureka Math Geometry Module 1
Eureka Math Geometry Module 1 employs a comprehensive assessment system to monitor and evaluate student progress.
Student progress is tracked through a combination of formative and summative assessments.
Formative Assessments
Formative assessments provide teachers with ongoing feedback on student understanding throughout the module.
- Exit tickets: Brief assessments at the end of each lesson to check for understanding.
- Warm-ups: Short activities at the beginning of lessons to review previous material and prepare students for new concepts.
- Observations: Teachers observe students during lessons to assess their engagement, participation, and problem-solving skills.
Summative Assessments, Eureka math geometry module 1
Summative assessments measure student mastery of module concepts at specific points in time.
- Module Assessments: Administered at the end of each module to assess overall understanding.
- End-of-Unit Assessments: Given at the end of each unit to evaluate students’ progress towards module goals.
- Performance Tasks: Projects or assignments that require students to demonstrate their understanding of geometry concepts through real-world applications.
Technology Integration in Eureka Math Geometry Module 1
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing the teaching and learning of geometry in Eureka Math Geometry Module 1. It provides interactive tools, visual representations, and collaborative platforms that support student engagement and deeper understanding of geometric concepts.
Eureka Math Geometry Module 1 is a comprehensive resource for learning the fundamentals of geometry. Its interactive lessons and exercises make learning engaging and effective. Like the characters in “The Gift of the Magi,” who selflessly sacrificed their most valuable possessions to make each other happy (read the answers here) , this module encourages students to explore geometry with a curious and open mind.
By the end of Module 1, students will have a strong foundation in geometric concepts and problem-solving skills.
Technology tools such as:
- Interactive whiteboards allow students to manipulate geometric figures and explore their properties.
- Geometer’s Sketchpad enables students to create dynamic constructions and investigate geometric relationships.
- Online simulations and applets provide interactive experiences that make abstract concepts more concrete.
Furthermore, technology supports student collaboration and communication. Online forums and discussion boards allow students to share ideas, ask questions, and engage in mathematical discourse with their peers and teachers. Social media platforms can be used to extend learning beyond the classroom and connect students with a broader community of mathematicians.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Eureka Math Geometry Module 1
Eureka Math Geometry Module 1 presents unique challenges for students. Understanding these challenges and implementing research-based solutions are crucial for effective instruction.
Student Challenges
- Difficulty in Visualizing Geometric Concepts:Students may struggle to visualize three-dimensional shapes and their properties.
- Limited Spatial Reasoning:Students may lack the ability to mentally manipulate and transform geometric figures.
- Confusion between Similar and Congruent Figures:Students often confuse the concepts of similar and congruent figures, leading to incorrect conclusions.
- Challenges with Measurement and Area Formulas:Students may struggle to understand the concepts of area and volume and apply formulas accurately.
- Lack of Prior Knowledge:Students may enter the module with insufficient prior knowledge in geometry, making it difficult to build on existing concepts.
Research-Based Solutions
- Use Manipulatives and Visual Aids:Hands-on activities with manipulatives and visual aids help students develop spatial reasoning and visualize geometric concepts.
- Incorporate Technology:Technology tools, such as dynamic geometry software, allow students to explore and manipulate geometric figures interactively.
- Provide Clear and Explicit Instruction:Teachers should provide clear explanations, definitions, and examples to help students understand geometric concepts.
- Foster Collaborative Learning:Encourage students to work in groups and discuss their understanding of geometric ideas, promoting peer learning and clarification.
- Address Prior Knowledge Gaps:Conduct diagnostic assessments to identify areas where students need additional support and provide targeted instruction to fill those gaps.
Successful Interventions
Successful interventions in Eureka Math Geometry Module 1 include:
- Use of Physical Models:Using physical models of geometric shapes helps students develop a deeper understanding of their properties.
- Integration of Hands-On Activities:Incorporating hands-on activities, such as constructing geometric shapes using straws and tape, reinforces concepts.
- Implementation of Technology-Enhanced Lessons:Utilizing technology-enhanced lessons, such as using interactive online simulations, engages students and enhances understanding.
- Peer Tutoring and Group Projects:Encouraging peer tutoring and group projects promotes collaboration and deepens conceptual understanding.
Real-World Connections in Eureka Math Geometry Module 1
Module 1 of Eureka Math Geometry establishes a solid foundation in geometric concepts that extend beyond theoretical understanding and find practical applications in various real-world contexts. This connection between geometry and everyday life not only enhances student engagement but also underscores the relevance and importance of the subject.
By exploring the properties and relationships of geometric shapes, students develop a deeper appreciation for the world around them. They recognize how geometry manifests in architectural designs, natural formations, and everyday objects, fostering a sense of wonder and curiosity.
Architecture and Design
- Students can analyze the geometric shapes and patterns used in buildings, bridges, and other structures. They can identify angles, triangles, and circles, understanding how these shapes contribute to structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
- By studying symmetry, students can appreciate the balance and harmony found in architectural designs, from ancient temples to modern skyscrapers.
Nature and the Environment
- Geometry is evident in the natural world, from the hexagonal cells of honeycombs to the spiral patterns of seashells. Students can explore these shapes, recognizing the mathematical principles that govern their formation.
- By understanding the geometry of plant growth, students can appreciate the efficiency and beauty of nature’s designs.
Everyday Objects
- Students can examine the geometric shapes found in everyday objects, such as the cylindrical shape of a can or the triangular shape of a traffic sign. They can analyze how these shapes serve specific purposes and contribute to the functionality of the object.
- By understanding the geometry of packaging, students can appreciate the efficient use of space and materials in product design.
Making these real-world connections not only enhances student understanding but also fosters their appreciation for the beauty and practicality of geometry. It transforms learning from an abstract concept to a meaningful and engaging experience.
Student Engagement Activities for Eureka Math Geometry Module 1
Supplement Module 1 lessons with engaging activities to spark student interest and deepen their understanding of geometry concepts.
Hands-on Experiments
Conduct hands-on experiments to provide students with concrete experiences that reinforce abstract geometric ideas.
- Use straws and pipe cleaners to create 3D shapes, allowing students to visualize and explore their properties.
- Experiment with different materials to demonstrate the concept of volume and surface area.
- Build a scale model of a geometric structure to illustrate real-world applications of geometry.
Games
Incorporate games into the learning process to make geometry fun and interactive.
- Play a geometry version of Bingo, where students match geometric terms to their definitions or properties.
- Create a scavenger hunt that requires students to identify and measure geometric shapes in the classroom or outdoors.
- Organize a “Geometry Olympics” with challenges such as shape identification, angle measurement, and volume estimation.
Problem-Solving Challenges
Pose problem-solving challenges to encourage students to apply their geometric knowledge and develop critical thinking skills.
- Present students with real-world scenarios that require them to use geometry to solve problems, such as calculating the area of a garden or the volume of a storage container.
- Create puzzles or riddles that involve geometric concepts, fostering logical reasoning and spatial visualization.
- Engage students in collaborative problem-solving activities, where they work together to solve complex geometric challenges.
FAQs
What is the primary focus of Eureka Math Geometry Module 1?
Establishing a solid foundation in geometry, covering concepts such as points, lines, angles, and shapes.
How does Module 1 align with Common Core State Standards?
It aligns with specific standards related to geometry, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive curriculum.
What are some effective teaching strategies for Module 1 lessons?
Incorporating hands-on activities, using manipulatives and visual aids, and differentiating instruction to meet diverse learning needs.